线索树
线索树(Threaded tree)
我们知道二叉查找树中的元素是有一定顺序的, 但是要将其中的元素排序, 需要有额外的高效方法. 在二叉树中对非满结点添加一些前后相继结点的信息, 得到所谓的线索树, 可以用来将二叉树中的结点进行排序.
在二叉树中, 每个叶子有两个空链接(left和right都是
因此, 二叉查找树中分配的这些指针有一半被浪费了. 现在设指针

This slide is based on the book of Mark Allen Weiss
张怀勇等译.
定义
一棵树是一些结点的集合. 这个集合可以是空集. 若不是空集, 则树由称为
实现树的一种办法是在每一个结点除数据外还要有一些链, 来指向该结点的每一个 child.
struct TreeNode
{
Object element;
TreeNode *firstChild;
TreeNode *nextSibling;
};
用于包括
伪代码
void FileSystem::listAll( int depth = 0 ) const
{
printName( depth ); // Print the name of the object
if( isDirectory( ) )
for each file c in this directory (for each child)
c.listAll( depth + 1 );
}
将下面的程序保存为
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
DIR *directory_pointer;
struct dirent *entry;
if((directory_pointer=opendir(argv[1]))==NULL)
{
printf("Error opening %s\n",argv[1]);
}
else
{
while( (entry=readdir(directory_pointer)) )
{
printf("%s\n",entry->d_name);
}
closedir(directory_pointer);
}
return 0;
}
showdir c:\windows
下面的例子递归地显示目录列表中的文件, 不过有问题, 请修正.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Dirent.h" //需要更改库中的 dirent.h, 加入下面几行, 然后不妨保存为 Dirent.h
/*
#define FA_ANY 0xff
#undef FA_DIREC
#define FA_DIREC 0x10
*/
#include <dos.h>
#include <io.h>
#include <direct.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXPATH 100
void show_directory(char *directory_name)
{
DIR *directory_pointer;
struct dirent *entry;
unsigned attributes;
if((directory_pointer=opendir(directory_name)) == NULL)
printf("Error opening %s\n", directory_name);
else
{
chdir(directory_name);
while(entry=readdir(directory_pointer))
{
attributes=_chmod(entry->d_name,0);
//Check if entry is for a subdirectory and is not "." or ".."
if((attributes & FA_DIREC) && (strncmp(entry->d_name,".",1)!=0))
{
printf("\n\n-----%s-----\n",entry->d_name);
show_directory(entry->d_name);
}else
printf("%s\n",entry->d_name);
}
closedir(directory_pointer);
chdir("..");
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//char buffer[MAXPATH];
//Save current directory so you can restore it later
//getcwd(buffer,sizeof(buffer));
show_directory(argv[1]);
//chdir(buffer);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <io.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <string.h>//如果去掉, 则编译会提示: warning: implicit declaration of function 'strncmp' [-Wimplicit-function-declaration]
#define MAXPATH 100
int isFolder(char* fileName);
void show_directory(char *directory_name, int depth);
void printTabString(int depth);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//char buffer[MAXPATH];
//Save current directory so you can restore it later
//getcwd(buffer,sizeof(buffer));
int depth=0;//记录当前目录的深度
if(argc < 2)
{
argv[1]=".";
}else if(argc > 2)
{
printf("\nUsage: showdir.exe \n");
}
show_directory(argv[1], depth);
//chdir(buffer);
return 0;
}
//return value: 1: folder, 0: file
int isFolder(char* fileName)
{
//char* fileName = "aa.txt";
struct _stat buf;
int value;
//int result;
//result = _stat( fileName, &buf );
_stat( fileName, &buf );
if(_S_IFDIR & buf.st_mode){
//printf("folder\n");
value=1;
}else if(_S_IFREG & buf.st_mode){
//printf("file\n");
value=0;
}
return value;
}
void show_directory(char *directory_name, int depth)
{
DIR *directory_pointer;
struct dirent *entry;
int _depth=depth;
//printf("depth=%d\n",_depth);
if((directory_pointer=opendir(directory_name)) != NULL)
{
//it is a directory
chdir(directory_name);
_depth++;
while( (entry=readdir(directory_pointer)) )
{
//对于 System Volume Information 文件夹, 下面的 _chmod 会失败.
//attributes=_chmod(entry->d_name,0);
//printf("d_name: %s\td_ino=%ld, d_namlen=%d, d_reclen=%d\n",entry->d_name,entry->d_ino, entry->d_namlen, entry->d_reclen);
if( (strncmp(entry->d_name,".",1)!=0) )
{
//对于 System Volume Information 文件夹
if(isFolder(entry->d_name))
{
printTabString(_depth);
printf("[%s]\n",entry->d_name);
show_directory(entry->d_name,_depth);
}
else
{
//is file
printTabString(_depth);
printf("%s","|-");
printf("%s\n",entry->d_name);
}
}else
{
printTabString(_depth);
printf("%s","|-");
printf("%s\n",entry->d_name);
}
}
}
closedir(directory_pointer);
chdir("..");
_depth--;
}
void printTabString(int depth)
{
if(depth <= 0)
{
return;
}
putchar('|');
while(depth > 0)
{
putchar(' ');
putchar(' ');
--depth;
}
}
适合Windows Visual Studio 编程的头文件
下载此文件, 并将其加入到工程中, 比如我们将其命名为
此外还需要加载
#include <direct.h>
并且要将之前代码中的
在前序遍历中, 对结点的处理工作是在它的诸 child 结点被处理之前进行的.
在后序遍历中, 在一个结点的工作是在它的诸 child 结点被计算之后进行的.
二叉树的一个重要应用是它们在查找中的应用. 树的每个结点存储一项数据. 这里为简单起见, 我们假设是整数, 并且所有项是互异的.
二叉树的每个结点 $X$, 如果它的左子树中的所有值小于 $X$ 中的值, 并且它的右子树中的所有值大于 $X$ 中的值, 则称此二叉树为
二叉查找树的平均深度是 $O(\log N)$, 所以一般不必担心栈空间被用尽.
template <typename Comparable>
class BinarySearchTree
{
public:
BinarySearchTree( );
BinarySearchTree( const BinarySearchTree & rhs );
~BinarySearchTree( );
const Comparable & findMin( ) const;
const Comparable & findMax( ) const;
bool contains( const Comparable & x ) const;
bool isEmpty( ) const;
void printTree( ) const;
void makeEmpty( );
void insert( const Comparable & x );
void remove( const Comparable & x );
const BinarySearchTree & operator=( const BinarySearchTree & rhs );
private:
struct BinaryNode
{
Comparable element;
BinaryNode *left;
BinaryNode *right;
BinaryNode( const Comparable & theElement, BinaryNode *lt, BinaryNode *rt )
: element( theElement ), left( lt ), right( rt ) { }
};
BinaryNode *root;
void insert( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode * & t );
void remove( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode * & t );
BinaryNode * findMin( BinaryNode *t ) const;
BinaryNode * findMax( BinaryNode *t ) const;
bool contains( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode *t ) const;
void makeEmpty( BinaryNode * & t );
void printTree( BinaryNode *t ) const;
BinaryNode * clone( BinaryNode *t ) const;
};
数据成员是指向根结点
/**
* Returns true if x is found in the tree.
*/
bool contains( const Comparable & x ) const
{
return contains( x, root );
}
/**
* Insert x into the tree; duplicates are ignored.
*/
void insert( const Comparable & x )
{
insert( x, root );
}
/**
* Remove x from the tree. Nothing is done if x is not found.
*/
void remove( const Comparable & x )
{
remove( x, root );
}
/**
* Internal method to test if an item is in a subtree.
* x is item to search for.
* t is the node that roots the subtree.
*/
bool contains( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode *t ) const
{
if( t == NULL )
return false;
else if( x < t->element )
return contains( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
return contains( x, t->right );
else
return true; // Match
}
注意测试的顺序, 首先要对是否为空树进行测试, 因为如果不那么做就会产生一个企图通过
其余的测试应该使得最不可能的情况安排在最后进行.
这里的两个递归调用事实上都是“尾递归”, 可以用一个
尾递归的使用是合理的, 因为算法表达式的简明性是以速度的降低为代价的, 而这里所使用的栈空间的量也只不过是 $O(\log N)$ 而已.
图 4-19 给出了使用函数对象而不是使用
template <typename Object, typename Comparator=less<Object> >
class BinarySearchTree
{
public:
// Same methods, with Object replacing Comparable
private:
BinaryNode *root;
Comparator isLessThan;
// Same methods, with Object replacing Comparable
/**
* Internal method to test if an item is in a subtree.
* x is item to search for.
* t is the node that roots the subtree.
*/
bool contains( const Object & x, BinaryNode *t ) const
{
if( t == NULL )
return false;
else if( isLessThan( x, t->element ) )
return contains( x, t->left );
else if( isLessThan( t->element, x ) )
return contains( x, t->right );
else
return true; // Match
}
};
这两个 private 例程分别返回指向树中包含最小元和最大元的结点的指针.
为执行
/**
* Internal method to find the smallest item in a subtree t.
* Return node containing the smallest item.
*/
BinaryNode * findMin( BinaryNode *t ) const
{
if( t == NULL )
return NULL;
if( t->left == NULL )
return t;
return findMin( t->left );
}
这种递归是如此简单, 以至于许多程序员不厌其烦地使用它. 思考一下, 能否不用递归? 怎么实现.
if(t==NULL) return NULL;
else{
while(t->left!=NULL)
{
t=t->left;
}
return t;
}
/**
* Internal method to find the largest item in a subtree t.
* Return node containing the largest item.
*/
BinaryNode * findMax( BinaryNode *t ) const
{
if( t != NULL )
while( t->right != NULL )
t = t->right;
return t;
}
进行插入操作的例程在概念上是很简单的. 为了将
/**
* Internal method to insert into a subtree.
* x is the item to insert.
* t is the node that roots the subtree.
* Set the new root of the subtree.
*/
void insert( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode * & t )
{
if( t == NULL )
t = new BinaryNode( x, NULL, NULL );
else if( x < t->element )
insert( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
insert( x, t->right );
else
; // Duplicate; do nothing
}
注意, 在递归例程中, 只有当一个新树叶生成时,
当这种情况发生时, 就说明递归例程被其他结点
重复元的插入可以通过在结点记录中保留一个附加字段以指示此数据元出现的频率来处理. 这使整棵树增加了某些附加空间, 但是, 却比将重复信息放到树中要好(它将使树的深度变得很大).
当然, 如果
同许多数据结构一样, 最困难的操作是删除.
/**
* Internal method to remove from a subtree.
* x is the item to remove.
* t is the node that roots the subtree.
* Set the new root of the subtree.
*/
void remove( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode * & t )
{
if( t == NULL )
return; // Item not found; do nothing
if( x < t->element )
remove( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
remove( x, t->right );
else if( t->left != NULL && t->right != NULL ) // Two children
{
t->element = findMin( t->right )->element;
remove( t->element, t->right );
}
else
{
BinaryNode *oldNode = t;
t = ( t->left != NULL ) ? t->left : t->right;
delete oldNode;
}
}
这里的
若使用C语言中的
//根据当前指针t最后一位的奇偶性决定是左删除还是右删除.
void removeByAddr( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode * & t )
{
if( t == NULL )
return; // Item not found; do nothing
if( x < t->element )
removeByAddr( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
removeByAddr( x, t->right );
else if( t->left != NULL && t->right != NULL ) // Two children
{//根据t中存储地址最后一位的奇偶性决定是左删除还是右删除.
if(t&1==1)
{//左删除
//从t的左子树中找到最大元的位置
//将最大元element覆盖当前节点t的element.
t->element=findMax(t->left)->element;
//虽然现在知道了右子树中最小元的位置, 但不能直接删除. 因为pt可能还有右子树.
removeByAddr(t->element, t->left);
}else{
//右删除
//从t的右子树中找到最小元并覆盖t的element
t->element=findMin(t->right)->element;
removeByAddr(t->element, t->left);
}
}
else
{
BinaryNode *oldNode = t;
t = ( t->left != NULL ) ? t->left : t->right;
delete oldNode;
}
}
如果删除的次数不多, 则通常使用的策略是
注: (有重复项的二叉查找树的remove方法本应该就这么做.)
位于
public:
/**
* Destructor for the tree
*/
~BinarySearchTree( )
{
makeEmpty( );
}
/**
* Make the tree logically empty.
*/
void makeEmpty( )
{
makeEmpty( root );
}
位于
private:
/**
* Internal method to make subtree empty.
* (recursive method)
*/
void makeEmpty( BinaryNode * & t )
{
if( t != NULL )
{
makeEmpty( t->left );
makeEmpty( t->right );
delete t;
}
t = NULL;
}
public:
/**
* Deep copy.
*/
const BinarySearchTree & operator=( const BinarySearchTree & rhs )
{
if( this != &rhs )
{
makeEmpty( );
root = clone( rhs.root );
}
return *this;
}
/**
* Internal method to clone subtree.
*
* 思考, 如何输出子树克隆过程中各个节点复制的次序?
*/
BinaryNode * clone( BinaryNode *t ) const
{
if( t == NULL )
return NULL;
else
{
//打印 t 结点, 从而知道次序
return new BinaryNode( t->element, clone( t->left ), clone( t->right ) );
}
}
我们知道二叉查找树中的元素是有一定顺序的, 但是要将其中的元素排序, 需要有额外的高效方法. 在二叉树中对非满结点添加一些前后相继结点的信息, 得到所谓的线索树, 可以用来将二叉树中的结点进行排序.
在二叉树中, 每个叶子有两个空链接(left和right都是
因此, 二叉查找树中分配的这些指针有一半被浪费了. 现在设指针

书本 P.134, Ex 4.49.
由于具有 $N$ 个结点的二叉查找树有 $N+1$ 个
具体的, 若一个结点(我们用指针
这些附加的链就是所谓的线索(thread).
要添加线索, 应在
不需要额外的栈或向量. 但是每个结点中新增了一个bool变量
线索树可以是“升序排列”, 如这里采用了
从 BinarySearchTree 的 insert 修改而来.
void insert( const Comparable & x, BinaryNode * & t, BinaryNode * nextThreadNode)
{
if( t == NULL )
{
t = new BinaryNode( x, NULL, nextThreadNode , true);
}
else if( x < t->element )
{
//现在的线索树是从小到大的顺序, 因此, 此时直接调用 insert()
insert( x, t->left, t );
}
else if( t->element < x )
{
//需要判断t是否是线索结点, 如果是, 则其右儿子为空, 可以插入新的结点.
if(t->rightThread)
{
//!!!
//此时 t 真实的右儿子为空, 因此第二个参数是 NULL,
//而 t 是线索结点, t->right 指向下一个结点, 因此作为第三个参数传递
insert( x, NULL, t->right );
}
}
else
; // Duplicate; do nothing
}
线索树可以用于多项式的按幂排列.
AVL 树是指带有
最简单的想法是要求左右子树始终具有相同高度.
另一种平衡条件是要求每个结点都必须有相同高度的左子树和右子树.
如果空树的高度定义为
因此, 虽然这种平衡条件保证了树的深度小, 但是它太严格, 使用面极小. 为此我们需要放宽条件.
上面的两颗二叉查找树中, 哪一个是 AVL 树?
在高度为
试求出 $S(h)$ 的具体表达式. (见问题2125 http://www.atzjg.net/admin/do/view_question.php?qid=2125)
当进行插入操作时, 需要更新通向根结点路径上那些结点的所有平衡信息, 而插入操作隐含着困难的原因在于, 插入一个结点可能破坏 AVL 树的特性.
如果发生这种情况, 那么就要恢复平衡的性质后才认为这一步插入操作完成.
事实上, 这总可以通过对树进行简单的修正来做到, 我们称其为
假设
给出 AVL树代码的一些参考文献.
#ifndef AVL_TREE_H
#define AVL_TREE_H
#include "dsexceptions.h"
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream> // For NULL
using namespace std;
// AvlTree class
//
// CONSTRUCTION: with ITEM_NOT_FOUND object used to signal failed finds
//
// ******************PUBLIC OPERATIONS*********************
// int height() --> get Height of the tree
// void insert( x ) --> Insert x
// void remove( x ) --> Remove x (unimplemented)
// bool contains( x ) --> Return true if x is present
// Comparable findMin( ) --> Return smallest item
// Comparable findMax( ) --> Return largest item
// boolean isEmpty( ) --> Return true if empty; else false
// void makeEmpty( ) --> Remove all items
// void printTree( ) --> Print tree in sorted order
// ******************ERRORS********************************
// Throws UnderflowException as warranted
//template <class Comparable> //这里写class或typename都可以
template <typename Comparable>
class AvlTree
{
public:
AvlTree( ) : root( NULL )
{ }
//注意, 这里root初始化为NULL会导致后面operator=() 不必进行makeEmpty(), 从而复制前的树中的结点未被清空. 导致内存泄露.
AvlTree( const AvlTree & rhs ) // : root( NULL )
{
*this = rhs;
}
~AvlTree( )
{
makeEmpty( );
}
/**
* height(), 返回该AVL树的高度
*/
int height() const
{
return height(root);
}
//前序遍历"AVL树"
void preOrderErgodic()
{
preOrderErgodic(root);
}
// 中序遍历"AVL树"
void midOrderErgodic()
{
midOrderErgodic(root);
}
// 后序遍历"AVL树"
void postOrderErgodic()
{
postOrderErgodic(root);
}
/**
* Find the smallest item in the tree.
* Throw UnderflowException if empty.
*/
const Comparable & findMin( ) const
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
throw UnderflowException( );
return findMin( root )->element;
}
/**
* Find the largest item in the tree.
* Throw UnderflowException if empty.
*/
const Comparable & findMax( ) const
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
throw UnderflowException( );
return findMax( root )->element;
}
/**
* Returns true if x is found in the tree.
*/
bool contains( const Comparable & x ) const
{
return contains( x, root );
}
/**
* Test if the tree is logically empty.
* Return true if empty, false otherwise.
*/
bool isEmpty( ) const
{
return root == NULL;
}
/**
* Print the tree contents in sorted order.
*/
void printTree( ) const
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
cout << "Empty tree" << endl;
else
printTree( root );
}
/**
* Make the tree logically empty.
*/
void makeEmpty( )
{
makeEmpty( root );
}
/**
* Insert x into the tree; duplicates are ignored.
*/
void insert( const Comparable & x )
{
insert( x, root );
}
/**
* Remove x from the tree. Nothing is done if x is not found.
* 非懒惰删除比较困难, 请实现懒惰删除.
*/
void remove( const Comparable & x )
{
AvlNode * t;
if( (t=search(root,x))!=NULL )
{
remove(root,t);
}
}
/**
* Deep copy.
*/
const AvlTree & operator=( const AvlTree & rhs )
{
if( this != &rhs )
{
makeEmpty( );
root = clone( rhs.root );
}
return *this;
}
private:
//struct 是默认 public 的 class
struct AvlNode
{
Comparable element;
AvlNode *left;
AvlNode *right;
int height;
AvlNode( const Comparable & theElement, AvlNode *lt,
AvlNode *rt, int h = 0 )
: element( theElement ), left( lt ), right( rt ), height( h ) { }
};
AvlNode *root;
public:
/**
* Returns the AVLNode pt if x is found in the tree.
*/
// (递归实现)查找AVL树中值为x的节点
AvlNode * recursiveSearch(const Comparable & x)
{
return recursiveSearch(root, x);
}
// (非递归实现)查找AVL树中值为x的节点
AvlNode * search(const Comparable & x)
{
return search(root, x);
}
private:
//前序遍历"AVL树"
void preOrderErgodic(AvlNode * & t)
{
if(t != NULL)
{
cout<< t->element << " ";
preOrderErgodic(t->left);
preOrderErgodic(t->right);
}
}
// 中序遍历"AVL树"
void midOrderErgodic(AvlNode * & t)
{
if(t != NULL)
{
preOrderErgodic(t->left);
cout<< t->element << " ";
preOrderErgodic(t->right);
}
}
// 后序遍历"AVL树"
void postOrderErgodic(AvlNode * & t)
{
if(t != NULL)
{
preOrderErgodic(t->left);
preOrderErgodic(t->right);
cout<< t->element << " ";
}
}
/**
* Internal method to insert into a subtree.
* x is the item to insert.
* t is the node that roots the subtree.
* Set the new root of the subtree.
*/
//在 t 所指的结点处插入一个结点, 值为x
void insert( const Comparable & x, AvlNode * & t )
{
if( t == NULL )
{
t = new AvlNode( x, NULL, NULL );
}
else if( x < t->element )
{
insert( x, t->left );//注意这里调用时会传递第二个参数的值, 也即 t 的值会变化.
if( height( t->left ) - height( t->right ) == 2 )
{
if( x < t->left->element )
{//左-左 ==> 则进行右旋转
rotateWithLeftChild( t );
}
else
{//左-右. 则先左旋转, 后右旋转
doubleWithLeftChild( t );
}
}
}
else if( t->element < x )
{
insert( x, t->right );
if( height( t->right ) - height( t->left ) == 2 )
{
if( t->right->element < x )
{
rotateWithRightChild( t );
}
else
{
doubleWithRightChild( t );
}
}
}
else
; // Duplicate; do nothing
//更新 t 结点处的高度
t->height = max( height( t->left ), height( t->right ) ) + 1;
}
/**
* Internal method to remove the item at the AvlNode ptX starting from AvlNode t.
* 这里的 remove 参考了 skywang12345 写的代码
* https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3577360.html#a2
* 但是实际上是有问题的.
* 可以举出例子说明这里的代码并没有很好的纠正不平衡性.
*/
AvlNode * remove(AvlNode * & t, AvlNode * ptX)
{
// 根为空 或者 没有要删除的节点,直接返回NULL。
if (t==NULL || ptX==NULL)
return NULL;
// 待删除的节点在t的左子树中
if (ptX->element < t->element)
{
t->left = remove(t->left, ptX);
// 删除节点后,若AVL树失去平衡,则进行相应的调节。
if (height(t->right) - height(t->left) == 2)
{// 此时看成在 t->right 中插入了结点
AvlNode * r = t->right;
if (height(r->left) > height(r->right))
{
t = doubleWithRightChild(t);
}
else
{
t = rotateWithRightChild(t);
}
}
}
else if (ptX->element > t->element)
{// 待删除的节点在t的右子树中
t->right = remove(t->right, ptX);
// 删除节点后,若AVL树失去平衡,则进行相应的调节。
if (height(t->left) - height(t->right) == 2)
{// 此时看成在 t->left 中插入了结点
AvlNode *l = t->left;
if (height(l->right) > height(l->left))
{
t = doubleWithLeftChild(t);
}
else
{
t = rotateWithLeftChild(t);
}
}
}
else
{// t是要删除的节点
// 如果t所指的结点两个儿子都非空
if ((t->left!=NULL) && (t->right!=NULL))
{
if (height(t->left) > height(t->right))
{
// 如果tree的左子树比右子树高;
// 则(01)找出t的左子树中的最大节点
// (02)将该最大节点的值赋值给t。
// (03)删除该最大节点。
AvlNode * _maxNode = findMax(t->left);
t->element = _maxNode->element;
t->left = remove(t->left, _maxNode);
}
else
{
// 如果t的左子树不比右子树高(即它们相等,或右子树比左子树高1)
// 则(01)找出t的右子树中的最小节点
// (02)将该最小节点的值赋值给t。
// (03)删除该最小节点。
// 这类似于用t的右子树中最小节点做t的替身;
// 采用这种方式的好处是:删除t的右子树中最小节点之后,AVL树仍然是平衡的。
AvlNode * _minNode = findMin(t->right);
t->element = _minNode->element;
t->right = remove(t->right, _minNode);
}
}
else
{//t所指的结点只有一个儿子或没有儿子.
AvlNode * tmp = t;
//t->left 和 t->right 哪个非空, 就将 t 下移到哪个.
t = (t->left!=NULL) ? t->left : t->right;
//比如当 t->left 非空时, t->left 中的值覆盖 t.
//而这个t的值是原t结点父亲link所指的值, 现在的值被替换为t->left的值.
//从而实现了原t结点父亲指向了原t结点的左儿子.
//TO DO!!! 待处理, tmp的父结点的link得指向t
delete tmp;
}
}
//更新t结点的高度
t->height=max(height(t->left), height(t->right))+1;
return t;
}
//这是教材(第四版)中提供的remove方法
/**
* 从子树实施删除的内部方法
* x 是要被删除的项
* t 为该子树的根结点
* 设置该子树的新根
*/
void remove(const Comparable & x, AvlNode * & t)
{
if(t==nullptr)
return; //子树是空树, 则什么也不用做
if(x < t->element)
remove(x, t->left);
else if(t->element < x)
remove(x, t->right);
else if(t->left!=nullptr && t->right != nullptr)//两个儿子
{
t->element=findMin(t->right)->element;
remove(t->element, t->right);
}else
{
AvlNode * oldNode =t;
t=(t->left !=nullptr)?t->left:t->right;
delete oldNode;
}
balance(t);
}
//假设子树 t 是平衡的, 或刚破坏平衡条件, 即t的左子树和右子树高度之差的绝对值为1
void balance(AvlNode * & t)
{
if(t==nullptr)
return ;
//注意t->left==nullptr时, height(t->left)=-1,从而下面的if条件为false.
if(height(t->left)-height(t->right)>ALLOWED_IMBALANCE)
{//即下面的t->left==nullptr在这里不会出现, 从而编译不会有问题.
if(height(t->left->left)>=height(t->left->right))
rotateWithLeftChild(t);
else
doubleWithLeftChild(t);
}else
if(height(t->right)-height(t->left)>ALLOWED_IMBALANCE)
{
if(height(t->right->right)>=height(t->right->left))
rotateWithRightChild(t);
else
doubleWithRightChild(t);
}
t->height=max(height(t->left), height(t->right))+1;
}
/**
* Internal method to find the smallest item in a subtree t.
* Return node containing the smallest item.
*/
AvlNode * findMin( AvlNode *t ) const
{
if( t == NULL )
return NULL;
if( t->left == NULL )
return t;
return findMin( t->left );
}
/**
* Internal method to find the largest item in a subtree t.
* Return node containing the largest item.
*/
AvlNode * findMax( AvlNode *t ) const
{
if( t != NULL )
while( t->right != NULL )
t = t->right;
return t;
}
/**
* Internal method to test if an item is in a subtree.
* x is item to search for.
* t is the node that roots the tree.
*/
bool contains( const Comparable & x, AvlNode *t ) const
{
if( t == NULL )
return false;
else if( x < t->element )
return contains( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
return contains( x, t->right );
else
return true; // Match
}
/****** NONRECURSIVE VERSION*************************
bool contains( const Comparable & x, AvlNode *t ) const
{
while( t != NULL )
if( x < t->element )
t = t->left;
else if( t->element < x )
t = t->right;
else
return true; // Match
return false; // No match
}
*****************************************************/
//这里的recursiveSearch() 使用了递归
AvlNode * recursiveSearch(AvlNode * t, const Comparable & x) const
{//注意当 t==NULL 时, 后面的 t->element==x不会检查, 从而不会出现编译错误.
if (t==NULL || t->element==x)
return t;
if (x < t->element)
return recursiveSearch(t->left, x);
else
return recursiveSearch(t->right, x);
}
//非递归实现的查找
AvlNode * search(AvlNode * t, const Comparable & x) const
{
while ((t!=NULL) && (t->element!=x))
{
if (x < t->element)
t = t->left;
else
t = t->right;
}
return t;
}
/**
* Internal method to make subtree empty.
*/
void makeEmpty( AvlNode * & t )
{
if( t != NULL )
{
makeEmpty( t->left );
makeEmpty( t->right );
delete t;
}
t = NULL;
}
/**
* Internal method to print a subtree rooted at t in sorted order.
*/
/*
void printTree( AvlNode *t ) const
{
if( t != NULL )
{
printTree( t->left );
cout << t->element << endl;
printTree( t->right );
}
}
*/
void printTree(AvlNode * t) const
{
if(t != NULL)
{
cout << t->element << " ";
printTree(t->left);
printTree(t->right);
}
}
/**
* Internal method to clone subtree.
*/
AvlNode * clone( AvlNode *t ) const
{
if( t == NULL )
return NULL;
else
return new AvlNode( t->element, clone( t->left ), clone( t->right ), t->height );
}
// Avl manipulations
/**
* Return the height of node t or -1 if NULL.
*/
int height( AvlNode *t ) const
{
return t == NULL ? -1 : t->height;
}
int max( int lhs, int rhs ) const
{
return lhs > rhs ? lhs : rhs;
}
/**
* Rotate binary tree node with left child.
* For AVL trees, this is a single rotation for case 1.
* Update heights, then set new root.
* 书本原来返回类型为 void, 现在改为 AvlNode *
* rotateWithLeftChild() 右旋转
*/
AvlNode * rotateWithLeftChild( AvlNode * & k2 )
{
AvlNode *k1 = k2->left;
k2->left = k1->right;
k1->right = k2;
k2->height = max( height( k2->left ), height( k2->right ) ) + 1;
k1->height = max( height( k1->left ), k2->height ) + 1;
k2 = k1;
return k1;
}
/**
* Rotate binary tree node with right child.
* For AVL trees, this is a single rotation for case 4.
* Update heights, then set new root.
* 书本原来返回类型为 void, 现在改为 AvlNode *
* rotateWithRightChild() 左旋转
*/
AvlNode * rotateWithRightChild( AvlNode * & k1 )
{
AvlNode *k2 = k1->right;
k1->right = k2->left;
k2->left = k1;
k1->height = max( height( k1->left ), height( k1->right ) ) + 1;
k2->height = max( height( k2->right ), k1->height ) + 1;
k1 = k2;
return k2;
}
/**
* Double rotate binary tree node: first left child.
* with its right child; then node k3 with new left child.
* For AVL trees, this is a double rotation for case 2.
* Update heights, then set new root.
* 书本原来返回类型为 void, 现在改为 AvlNode *
*/
AvlNode * doubleWithLeftChild( AvlNode * & k3 )
{
rotateWithRightChild( k3->left );
return rotateWithLeftChild( k3 );
}
/**
* Double rotate binary tree node: first right child.
* with its left child; then node k1 with new right child.
* For AVL trees, this is a double rotation for case 3.
* Update heights, then set new root.
* 书本原来返回类型为 void, 现在改为 AvlNode *
*/
AvlNode * doubleWithRightChild( AvlNode * & k1 )
{
rotateWithLeftChild( k1->right );
return rotateWithRightChild( k1 );
}
};
#endif
本节描述一种相对简单的数据结构, 叫做
一般的, 当 $M$ 次操作的序列总的最坏情形运行时间为
因此, 一棵伸展树每次操作的摊还代价是
摊还分析 (amortized analysis) 是一种分析一个操作序列中所执行的所有操作的平均时间分析方法。
对于二叉查找树来说, 每次操作最坏情形时间
任何一次访问, 即使花费
二叉查找树的问题在于, 虽然一系列访问整体都是不好的操作有可能发生, 但是很罕见. 此时, 累积的运行时间很重要.
如果任意特定操作可以有最坏时间界
比如要访问一棵树的某个结点
伸展(splaying)的方法类似于上面介绍的旋转的想法, 不过在旋转如何实施上稍微有些选择的余地.
我们仍然从底向上沿着访问路径旋转. 令
伸展操作不仅将访问的结点移动到根处, 而且还有把访问路径上的大部分结点的深度大致减少一半的效果. 某些浅的结点最多向下推两个层次.
这些图着重强调了伸展树基本的和关键的性质.
伸展树有几种变体. 参见第12章.
按顺序打印二叉查找树的例程
/**
* Print the tree contents in sorted order.
*/
void printTree( ostream & out = cout ) const
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
out << "Empty tree" << endl;
else
printTree( root, out );
}
/**
* Internal method to print a subtree rooted at t in sorted order.
*/
void printTree( BinaryNode *t, ostream & out ) const
{
if( t != NULL )
{
printTree( t->left, out );
out << t->element << endl;
printTree( t->right, out );
}
}
使用后序遍历计算树的高度的例程
/**
* Internal method to compute the height of a subtree rooted at t.
*/
int height( BinaryNode *t )
{
if( t == NULL )
return -1;
else
return 1 + max( height( t->left ), height( t->right ) );
}
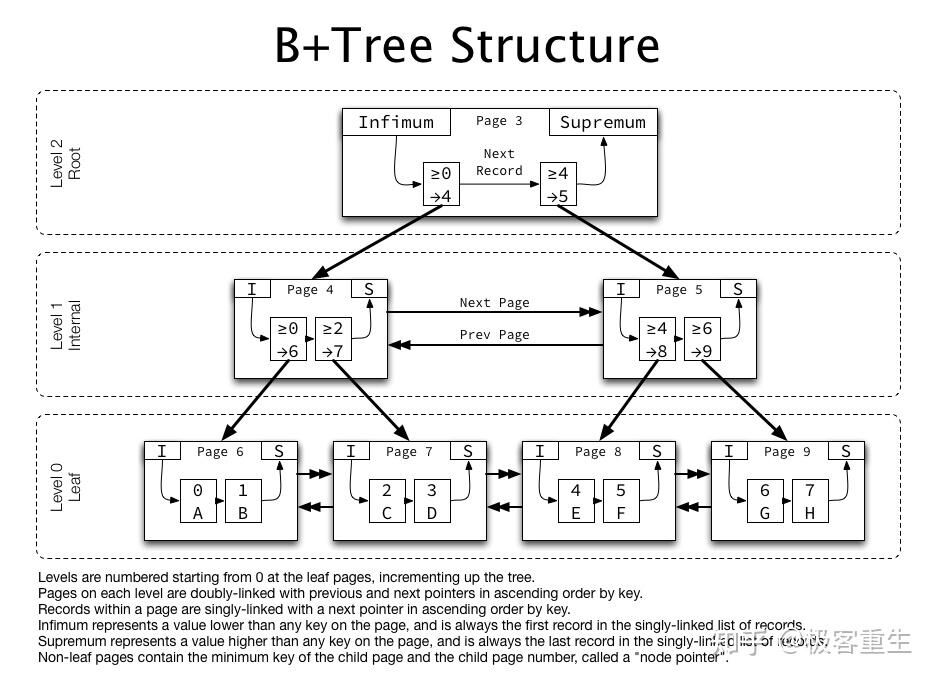
B 树主要用于数据库和文件系统.
迄今为止, 我们始终假设可以把整个数据结构存储到计算机的主存中. 但如果数据太多, 主存装不下时, 那么意味着必须把数据结构放到磁盘上.
此时时间计算中大O模型不再适用, 因为在大O分析中, 我们假设所有的操作花费同等的时间. 但现在这样假设不再合适, 特别是涉及到磁盘I/O的时候.
例如, 一台 500 MIPS 的机器每秒执行 5 亿条指令. IPS (Instructions per second) 是衡量处理器速度的一个指标. 比如: 1996 年, Intel Pentium Pro, 541 MIPS at 200 MHz. 这是相当快的, 主要是因为速度主要依赖于电的特性. 另一方面, 磁盘是机械运动的, 它的速度主要依赖于转动磁盘和移动磁头的时间. 许多磁盘以 7200 RPM 旋转, 也就是每分钟 7200 转, 1转占用1/120秒, 即 8.3ms. 平均认为磁盘转到一半的时候发现要寻找的信息; 因此如果忽略其他因素, 那么可以得到访问时间为 8.3ms(这是非常宽松的估计; 9-11ms 的访问时间更为常见). 因此, 每条大约可以进行120次磁盘访问. 若不和处理器的速度比较, 那么这听起来还是相当不错的.
阶为
考虑一棵 5 阶 B 树. 所有的非叶子结点的儿子数都在 3 和 5 之间(从而有 2 到 4 个关键字). 根至多有两个儿子. 这里, 我们让 $L=5$. 每片树叶有 3 到 5 个数据项.
设 T 是一棵 $M$ 阶 B 树(即除根之外的所有非叶子结点, 至多有 $M$ 个儿子). 有 $n$ 层. (这里设根在第0层, 第1层是根的儿子, 至少有两个结点.) 则总的结点数 $N$ 为 \[ N= M^0+M^1+M^2+\cdots+M^{n-1}=2+\frac{1-M^n}{1-M} \] 非叶子结点数与叶子结点数的比值为 \[ \frac{1+\frac{M^n-1}{M-1}-M^{n-1}}{M^{n-1}}=\frac{M^{n-1}+M-2}{M^{n-1}(M-1)}\approx\frac{1}{M-1} \]
每个结点代表一个磁盘区块, 根据所存储的项数决定 $M$ 和 $L$. 例如, 设一个区块可容纳8192($=2^{13}$)字节. 每个关键字使用 32 个字节. 在一棵 $M$ 阶 B 树中, 有 $M-1$ 个关键字, 总数为 32M-32 字节. 由于 \[ 36*228-32 = 8176 < 8192 < 8212=36*229-32 \] 故取 $M=228$.
由于每个数据记录是 256 字节, 因此我们能够把 32 个记录装入一个区块中(8192/256=32). 于是选择 $L=32$. 这样就保证每片树叶有 16--32个数据记录以及除根之外每个内部结点至少以114(=228/2)种方式分叉. 如果有 1000万个记录, 则至多需要 625000(=10000000/16)片叶子结点. $114^3=1481544$, 故在最坏的情形, 也就是以114种方式分叉, 则树叶在第4层上(注意根节点至多是2分叉). 若总的结点数是 $N$, 则当根节点是$N$换句话说, 最快情形的访问次数近似地由 $\log_{M/2}N$ 给出. 这里叶子结点数是 625000, 可大致推出总的结点数 \[N=(625000*228-1)/227+1\approx 627754.29\] 于是 $\log_{M/2}N\approx\log_{114}627754\approx 2.8187$
代码来自https://www.programiz.com/dsa/b-tree
// Searching a key on a B-tree in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode {
int *keys;//该结点中保存的所有键, 组成一个数组.
int t;//2t为阶数, 即至多有2t个儿子
TreeNode **C;//指向一列TreeNode, 即TreeNode数组, 其中每个元素是TreeNode* 指针
int n;//结点中元素个数
bool leaf;//是否是叶子
public:
TreeNode(int temp, bool bool_leaf);
void insertNonFull(int k);
void splitChild(int i, TreeNode *y);
void traverse();
TreeNode *search(int k);
friend class BTree;
};
class BTree {
TreeNode *root;
int t;
public:
BTree(int temp) {
root = NULL;
t = temp;
}
void traverse() {
if (root != NULL)
root->traverse();
}
TreeNode *search(int k) {
return (root == NULL) ? NULL : root->search(k);
}
void insert(int k);
};
/*
* 插入新元素 k
*/
void BTree::insert(int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
{//如果B树是空树, 则直接新建一结点(当然是叶子结点)
root = new TreeNode(t, true);
root->keys[0] = k;//将此元素k设置为第0个键(key)
root->n = 1;//结点中元素个数为1.
} else
{//根非空
//如果root结点中元素个数等于 2*deg-1, 则可以直接插入
if (root->n == 2 * t - 1)
{
TreeNode *s = new TreeNode(t, false);
s->C[0] = root;//root作为第一个儿子
s->splitChild(0, root);//分裂root结点
int i = 0;
if (s->keys[0] < k)
i++;
s->C[i]->insertNonFull(k);
root = s;//将新生成的结点作为root结点
} else
{
root->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
}
/* 每个结点形如
* [v|key1|v|key2|v|key3|v]
* 这里有 2t-1 个key, 2t个指针(v代表指针)
*/
TreeNode::TreeNode(int t1, bool leaf1)
{
t = t1;
leaf = leaf1;
keys = new int[2 * t - 1];//生成具有2*t-1元素的键向量.
C = new TreeNode *[2 * t];//生成2*t个元素的TreeNode*数组
n = 0;
}
/*
* 遍历此结点中所有元素
*/
void TreeNode::traverse()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
//当leaf==true时,
std::cout << " " << keys[i];
}
//此时i==n
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
}
/*
* 在此结点中寻找 k=79, 这里 keys[]={72,78,83}
* [v|72|v|78|v|83|v| | ]
* | | | |
* 66 72 78 83
* 68 73 79 84
* 69 74 81 85
* 70 76
*/
TreeNode *TreeNode::search(int k)
{
int i = 0;
//找到k所在的keys[i]
while (i < n && k > keys[i])
i++;
//如果k等于此key,则就返回指向此结点的指针
if (keys[i] == k)
return this;
//如果并不等于此key, 并且此结点已经是叶子结点, 则意味着找不到.
if (leaf == true)
return NULL;
//如果不是叶子结点, 则从C[i]指向的结点开始搜寻k.
return C[i]->search(k);
}
/*
* 在非满的结点中插入元素k
*/
void TreeNode::insertNonFull(int k)
{
int i = n - 1;
//如果是叶子结点
if (leaf == true)
{
while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k)
{
keys[i + 1] = keys[i];
i--;
}
keys[i + 1] = k;//将k插入到正确位置
n++;//插入成功, 实际上插入的就是关键字. 故关键字数目加一,
}
else
{//当前结点不是叶子结点
while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k)
i--;
//此时i满足 keys[i]<=k. 即 k 在C[i+1]子树中.
if (C[i + 1]->n == 2 * t - 1)
{//若C[i+1]所指向的结点中关键字已经满了, 即儿子数达到2t
splitChild(i + 1, C[i + 1]);
if (keys[i + 1] < k)
i++;
}
C[i + 1]->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
/**
* 分裂当前结点中的儿子结点y
* =========================
*/
void TreeNode::splitChild(int i, TreeNode *y)
{
//既然从y处分裂一个结点, 那么新的结点与 y 同处于一层. 所以若 y是树叶, 则 z 也是树叶.
//因此传递的参数与y一致. y->t, 2t指y结点的最多儿子数.
TreeNode *z = new TreeNode(y->t, y->leaf);
//每个结点至多具有2t个指针,至多可以存放2t-1个key.
//分裂结点时, key 已经满, 因此有 2t-1 个元素, 算上即将插入的元素, 则有2t个元素
//将这2t个元素放到两个结点中, 每个结点有t个元素.
z->n = t - 1;
// [v|0|v|1|v|2|v|3|v|...|t-1|v|t|v|t+1|v|...|2t-2|v] v 代表指针
// [拷贝到 z ]
// 将y指向的结点中 keys[t], keys[t+1], ..., keys[2t-2] 都拷贝到 z 中
// 共计拷贝 t-1 个元素 (2t-2-t+1=t-1).
for (int j = 0; j < t - 1; j++)
z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + t];
//如果y结点不是叶子, 则需要将其一般的儿子拷贝到新的结点.
//即j=t,t+1,...,2t-1的儿子C[j]拷贝到 z->C[j]
if (y->leaf == false)
{
for (int j = 0; j < t; j++)
z->C[j] = y->C[j + t];
}
y->n = t - 1;//更新被分裂结点的关键字的个数.
//这里的C[] 是当前 TreeNode 中的C, 由此推出这里的函数 splitChild(i,y)
//的确是分裂的是当前结点的儿子y.
//将index为i+1,i+2,...,n的儿子右移一个位置.
for (int j = n; j >= i + 1; j--)
C[j + 1] = C[j];
C[i + 1] = z;//将新的结点z插入到正确的位置 i+1 上.
//将当前结点的指标为i,i+1,...,n-1的关键字也右移一个位置
for (int j = n - 1; j >= i; j--)
keys[j + 1] = keys[j];
keys[i] = y->keys[t - 1];//分裂后, 被分裂的结点最后一个关键字不需要了, 存放到其父结点(也就是当前结点)的keys[]数组中.
n++;//当前结点分裂成功, 关键字数目加1.
}
int main() {
BTree t(3);
t.insert(8);
t.insert(9);
t.insert(10);
t.insert(11);
t.insert(15);
t.insert(16);
t.insert(17);
t.insert(18);
t.insert(20);
t.insert(23);
cout << "The B-tree is: ";
t.traverse();
int k = 10;
(t.search(k) != NULL) ? cout << endl
<< k << " is found"
: cout << endl
<< k << " is not Found";
k = 2;
(t.search(k) != NULL) ? cout << endl
<< k << " is found"
: cout << endl
<< k << " is not Found\n";
}
https://dichchankinh.com/~galles/visualization/BTree.html
之前讨论了 STL 中的容器
在使用
namespace std{
template <class T,
class Compare=less<T>,
class Allocator=allocator<T> >
class set;
template <class T,
class Compare=less<T>,
class Allocator=allocator<T> >
class multiset;
}
许多用于访问
图 3-6 中的 printCollection 函数模板在传递的参数为
template <typename Container>
void printCollection( const Container & c, ostream & out = cout )
{
if( c.empty( ) )
out << "(empty)";
else
{
typename Container::const_iterator itr = c.begin( );
out << "[ " << *itr++; // Print first item
while( itr != c.end( ) )
out << ", " << *itr++;
out << " ]" << endl;
}
}
因为
事实上,
要使得返回内容包含上面复杂的内容, 我们可以考虑
下面是两个不同的
pair<iterator,bool> insert( const Object & x);
pair<iterator,bool> insert( iterator hint, const Object & x);
set<int> s; for(int i=0; i<1000000;i++) s.insert(s.end(),i);
int erase(const Object & x); iterator erase(iterator itr); iterator erase(iterator start, iterator end);
对于查找,
iterator find(const Object & x) const;
默认情况下, 排序操作使用
另一种可替代的排序方案可以通过具有函数对象类型的
set<string, CaseInsensitiveCompare> s;
s.insert("Hello");
s.insert("HeLLo");
cout << "The size is: " << s.size() << endl;
这里的
class CaseInsensitiveCompare
{
public:
bool isLessThan( const string & lhs, const string & rhs) const
{
return stricmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) < 0;
}
}
| 操作 | 效果 |
|---|---|
count(elem) |
返回元素值为 |
find(elem) |
返回元素值为 |
lower_bound(elem) |
返回 |
upper_bound(elem) |
返回 |
equal_range(elem) |
返回 |
// set::lower_bound/upper_bound
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
int main ()
{
std::set<int> myset;
std::set<int>::iterator itlow,itup;
for (int i=1; i<10; i++) myset.insert(i*10); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
itlow=myset.lower_bound (30); // ^
itup=myset.upper_bound (60); // ^
//删除itlow 至 itup 之间的元素. 注意 itup 所指元素不包括在删除范围内. 可以理解为 [itlow, itup)
myset.erase(itlow,itup); // 10 20 70 80 90
std::cout << "myset contains:";
for (std::set<int>::iterator it=myset.begin(); it!=myset.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
换句话说, 对于
幸运的是,
ValueType & operator[] ( const KeyType & key );
这些语法不允许修改函数版本的
这里举了两个访问
map<string,double> salaries;
salaries[ "Pat" ] = 75000.00;//这里等号的左边调用了operator[], 因此插入了键为"Pat", 值为0的一个项到 salaries 这个 map 中. 同时返回指向这个 double 类型对象的引用. 然后第二步, 赋值将 map 中键为 "Pat" 的 double 对象改为 75000.
cout << salaries[ "Pat" ] << endl; // 输出这个 double 类型的对象, 值为 75000
cout << salaries[ "Jan" ] << endl; // 这里插入配对 "Jan" 和 0.0 到 salaries 这个 map 中, 并打印出来. 但是打印的结果可能不是 0.0, 这取决于应用程序.
/* 如果判断一个项是否在 map 中非常重要, 那么可以使用下面的方法.
*
*/
map<string,double>::const_iterator itr;
itr = salaries.find( "Chris" ); //如果键 Chris 没有找到, 则返回末端标识(salaries.end()).
if( itr == salaries.end( ) )
cout << "Not an employee of this company!" << endl;
else
cout << itr->second << endl; // 输出 itr 指向的 double 类型的对象, 这里的 itr 是 const_iterator 类型, 因此不能赋值.
map是c++的一个标准容器,它提供了很好的一对一的关系,在一些程序中建立一个map可以起到事半功倍的效果. 这里总结了map 的一些基本简单实用的操作!
map<string,int>mapstring; map<int,string>mapint; map<sring,char>mapstring; map<char,string>mapchar; map<char,int>mapchar; map<int,char>mapint;
2. map添加数据;
map<int,string> maplive; maplive.insert(pair<int,string>(102,"aclive")); maplive.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(321,"hai")); maplive[112]="April";//map中最简单最常用的插入添加!
3. map中元素的查找:
find()函数返回一个迭代器指向键值为key的元素,如果没找到就返回指向map尾部的迭代器。
map<int,string>::iterator itr;
itr=maplive.find(112);
if(itr==maplive.end())
cout << "we do not find 112" << endl;
else
cout << "we find 112" << endl;
4. map中元素的删除: 如果删除112;
map<int,string>::iterator itr;
itr=maplive.find(112);
if(itr==maplive.end())
cout<<"we do not find 112"<<endl;
else
maplive.erase(l_it); //delete 112;
5. map中 swap的用法: Map中的swap不是一个容器中的元素交换,而是两个容器交换; For example:
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
map <int, int> m1, m2, m3;
map <int, int>::iterator m1_Iter;
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 1, 10 ) );
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 2, 20 ) );
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 3, 30 ) );
m2.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 10, 100 ) );
m2.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 20, 200 ) );
m3.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 30, 300 ) );
cout << "The original map m1 is:";
for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
cout << " " << m1_Iter->second;
cout << "." << endl;
// This is the member function version of swap
//m2 is said to be the argument map; m1 the target map
m1.swap( m2 );
cout << "After swapping with m2, map m1 is:";
for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second;
cout << "." << endl;
cout << "After swapping with m2, map m2 is:";
for ( m1_Iter = m2.begin( ); m1_Iter != m2.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second;
cout << "." << endl;
// This is the specialized template version of swap
swap( m1, m3 );
cout << "After swapping with m3, map m1 is:";
for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second;
cout << "." << endl;
}
6. map的sort问题: Map中的元素是自动按key升序排序,所以不能对map用sort函数: For example:
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
map <int, int> m1;
map <int, int>::iterator m1_Iter;
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 1, 20 ) );
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 4, 40 ) );
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 3, 60 ) );
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 2, 50 ) );
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 6, 40 ) );
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 7, 30 ) );
cout << "The original map m1 is:" << endl;
for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
cout << m1_Iter->first << " " << m1_Iter->second << endl;
}
The original map m1 is: 1 20 2 50 3 60 4 40 6 40 7 30 请按任意键继续. . .
7. map的基本操作函数:
C++ Maps是一种关联式容器,包含“关键字/值”对
begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器
clear() 删除所有元素
count() 返回指定元素出现的次数
empty() 如果map为空则返回true
end() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器
equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对
erase() 删除一个元素
find() 查找一个元素
get_allocator() 返回map的配置器
insert() 插入元素
key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数
lower_bound() 返回键值大于等于给定元素的第一个位置
max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数
rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器
rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器
size() 返回map中元素的个数
swap() 交换两个map
upper_bound() 返回键值大于给定元素的第一个位置
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> Employees;
// 1) Assignment using array index notation
Employees[5234] = "Mike C.";
Employees[3374] = "Charlie M.";
Employees[1923] = "David D.";
Employees[7582] = "John A.";
Employees[5328] = "Peter Q.";
cout << "Employees[3374]=" << Employees[3374] << endl << endl;
cout << "Map size: " << Employees.size() << endl;
for( map<int,string>::iterator ii=Employees.begin(); ii!=Employees.end(); ++ii)
{
cout << (*ii).first << ": " << (*ii).second << endl;
}
}
#include <set>
string match="";
set<string> matches;
match='';
if(matches.find(match)!=matches.end())
{}else{
matches.insert(match);
outfile << match <
在实现
有几种可能的解决方案, 其中的一部分例举如下: